
Each of these career paths requires candidates to pass an exam and acquire an IRS preparer tax identification number (PTIN). Enrolled Agents (EAs) must pass a comprehensive three-part exam administered by the IRS, covering federal tax planning, individual and business tax return preparation, and representation. They must also complete 72 hours of continuing professional education (CPE) every three years. As long as a CPA or tax preparer has their preparer tax identification number (PTIN), they can help prepare and file your taxes. However, as the IRS notes, tax professionals have different levels of skills, education, and expertise, so always double-check your tax returns before filing them.
- It’s important to consider the long-term benefits and potential cost savings when making a decision between a tax preparer and a CPA.
- Business owners with simple tax filing needs can rely on a tax preparer.
- But the extra cost is often worth it for complex tax situations or if you need long-term planning.
- They abide by the professional ethics and moral code of conduct established by the state boards.
What Are the Working Conditions for a Tax Accountant?

They stay up-to-date with the ever-changing tax laws and regulations, ensuring that their clients maximize their tax savings while remaining compliant. CPAs carefully analyze financial data, identify deductions and credits, and prepare accurate tax returns. They also provide valuable advice on tax strategies, helping individuals and businesses minimize their tax liabilities. But a CPA isn’t the only professional who can file taxes on your behalf.
- The IRS doesn’t impose any education, experience, or licensing requirement for tax preparers to practice.
- Unlike CPAs, EAs’ expertise is limited to tax matters, making them extremely well versed in their specialty.
- While both involve working with taxes and finances, their roles, responsibilities, and qualifications differ significantly.
- A tax preparer usually handles basic tax filings, while a CPA offers a wider range of services.
- Tax preparers typically cost less to work with than a CPA, since they largely only offer tax preparation services.
What Are Representation Rights, and When Do You Need Them?
Most jurisdictions do not require candidates for the bar examination to have any particular type or amount of professional experience. However, insiders commonly note that earning professional experience as a paralegal, legal assistant, law clerk, or researcher can help. State bar examinations are very difficult, and insights gained from professional experience may improve your chances of passing. You can become an enrolled agent without professional experience by passing the three-part Special Enrollment Exam (SEE) issued by Food Truck Accounting the IRS. However, you can also follow an alternative, experience-based path. This path requires you to have a minimum of five years’ experience working for the IRS in any capacity that involves interpretation of taxation statutes.
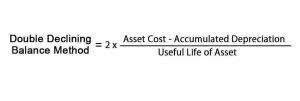
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Financial Needs
Apart from fining returns, CPAs can help you with tax planning too. They ensure you have minimum tax liability while abiding by the law. Moreover, if you value affordability and convenience, tax preparers often have more flexible schedules and lower fees compared to CPAs. They can provide unearned revenue you with personalized attention and guidance, making the tax preparation process less daunting. A tax preparer can be a great choice if your financial situation is relatively simple.


The IRS doesn’t impose any education, experience, or licensing requirement for tax preparers to practice. It started the Registered Tax Return Preparer Competency Test for regulating tax preparers in 2011. Therefore, you don’t have to pass any test to practice as a tax preparer. Moreover, with a regulatory body overlooking their work, chances of their committing fraud are greatly reduced.
Additionally, tax preparers may also offer tax planning advice to help clients reduce their tax liabilities in future years. An enrolled agent (EA) is an individual who can represent taxpayers to the Internal tax preparer vs cpa Revenue Service (IRS). In addition to preparing and filing tax returns, enrolled agents can assist clients with IRS audits. To become an enrolled agent, you must pass a three-part exam administered by the IRS. You do not have to be an accountant or CPA to be eligible to take the exam. To hold unlimited representation rights, tax preparers must earn certification as EAs, CPAs, or attorneys.
